There are many types of insulation used throughout the world in many different applications. The types of insulation materials used include foams (polystyrene, polyurethane, polyisocyanurate and polyethylene), fibers (glass, mineral wool, cellulose, silica), and powders.
Summary
These materials are used in many different configurations. Among those are semi-rigid to rigid boards, blocks, blown-in materials, and vacuum panels. The best insulation depends on the particular application.
Insulation is used to reduce energy flow in a number of different applications. Primary uses include construction, appliances, and transportation of goods. The performance of insulation is measured commonly by two factors, R-value and thermal conductivity. R-value is commonly used when discussing insulation used in building and construction. In the case of R value, the higher the number the better the insulator. Thermal conductivity value is more frequently used when discussing transportation of goods and scientific applications, particularly in pharma and life-science products. Thermal conductivity is the rate at which heat is transferred through a material. The lower the thermal conductivity value, the better the insulator. In this whitepaper, we will address the use of vacuum insulation panels in the transport of pharma and life-science products.
When long duration temperature control is required, VIP is a superior insulation. There are four main factors that the determine the performance of VIP with regards to its effectiveness as an insulator, the barrier film, the core material, desiccants/getters, and the vacuum level.
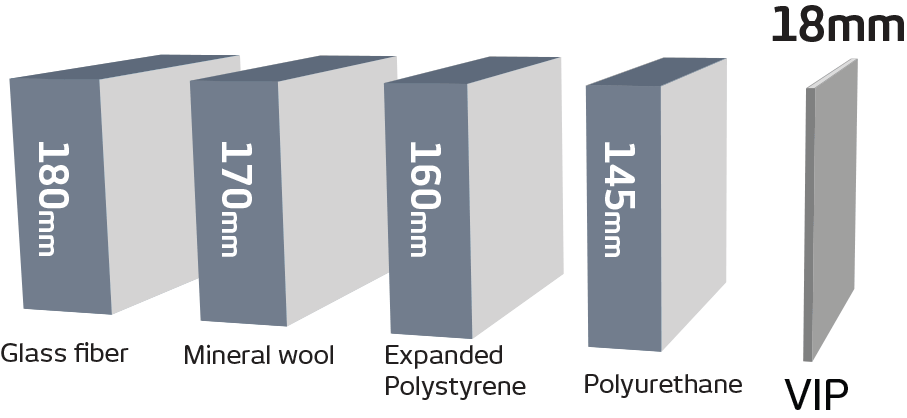
Image Courtesy of Avery Dennison-Hanita.
The Vacuum Level
The vacuum level is the first letter of the term VIP (Vacuum Insulated Panel). Vacuum is defined as a space without any particles. The effectiveness of a vacuum in maintaining a temperature can be demonstrated by the traditional thermos container that would keep your favorite beverage hot or cold all day long or the thermos that would keep your soup hot or favorite dessert cold until it was time to eat. This same theory is what minimizes the transfer of energy from one side of a vacuum insulated panel to the other. This is what keeps the cold on one side and warm on the other. During the manufacturing process of making VIP the space between the two layers of the barrier film is evacuated to remove as much of the air and water vapor particles as possible. The vacuum is measured in relation to atmospheric pressure. The greater the difference between the interior VIP pressure and atmospheric pressure, the better the performance of the VIP will be.
The Barrier Film
The material that separates the inside of the VIP from the outside atmosphere and maintains the vacuum is the barrier film. The purpose of the barrier film is to minimize the transfer of particles (air and water vapor) between the inside of the VIP and the outside, hence maintaining the vacuum. Generally two pieces of barrier film are used and sealed together to form an envelope. The film structure layer(s) provides a barrier as discussed, as well as a sealing layer to ensure no leakage takes place between the panel inner and outer layers. The barrier film also contains the core material on the inside of the envelope and helps define the shape of the panel. The barrier film is usually a multi-layer laminate structure, potentially comprised of many different types of materials.
Examples of different materials commonly used are polypropylene, polyethylene, nylon, aluminum, PET (polyethylene terephthalate), and combinations thereof. These layers are combined to provide the most effective barrier to prevent transfer of particles from the outside to the inside. Many different combinations are used depending on the specific requirements and desires of the manufacturer in anywhere from single layer to as many as seven to nine layers.
An additional concern of designers is the ‘edge effect’ caused by the type of barrier film used. Many of the more effective barrier film structures use metallic material layers which are very good barriers to prevent particle transfer. On the downside, these metallic layers are also very good conductors of energy. These layers can transfer energy from one side, around the edge of the VIP to the other side (edge effect), and essentially defeat much of the purpose of the VIP. There are many different methods of minimizing or preventing this ‘edge effect’ from taking place by modifying the layers of the barrier film and even using different types of film on each side of the VIP. The best barrier films will provide an effective vacuum barrier as well as minimize the edge effect.
The Core Material
The third major component of vacuum insulated panels is the core material. The core material must be dense enough to maintain its shape in a vacuum but not so dense as to transfer energy through the thickness of the panel. Through the years, many different materials have been used for the core component in vacuum panels. These materials include glass fibers, silica fibers, foams, mineral and glass wool, as well as powders, both fumed or pyrogenic silica and silica aerogels. The best core materials are microporous structures that do not provide a continuous path for energy to transfer from one surface to the other surface and actually disrupt the energy flow. A microporous structure allows all the particles that would transfer energy to be removed during the evacuation process. A good core material will also provide consistent and tight dimensional stability and withstand the pressure from the vacuum level in the panel. Dimensional stability will allow consistent dimensions and provide for a good tight fit when building boxes and shipping containers utilizing VIP.
The Desiccant and/or Getter
The fourth essential component of vacuum insulated panels is a desiccant and/or getter. The purpose of these components is to absorb any water vapor (desiccant) or gaseous particles (getter) that may still be present inside the vacuum panel as well as absorb those particles that may enter the sealed panel through the seam or due to permeability of the barrier film material. There are many different types of materials used for desiccants and getters, among those being calcium oxide, zeolite, and silica gel. Getters can be designed for the specific gases they are intended to absorb.
Conclusion
The choice of VIP materials can be tailored for each application. It has been demonstrated that thermal conductivities of down to 1.15 mW/mK (R >95) are possible with the proper combination of micro glass fiber core material, vacuum level, desiccants/getters and the barrier film structure. Consideration for longevity, durability, insulation level and cost will help determine which type of VIP is best for a given application.
To learn more about how you can benefit from CSafe’s service offering, get in touch.
Your nearest sales representative is ready to help you maximize the impact of your life-saving therapeutics.